BrandXR Research Report: How Beauty Brands Are Using AR Mirrors to Increase Sales
Executive Summary
This report examines the business case for in-store AR mirrors, the technology and ecosystem, and detailed case studies of successful implementations. For comprehensive market intelligence, this report complements our broader 2025 Augmented Reality in Retail & E-Commerce Research Report, which examines AR adoption across all retail categories, and our Business Case for Augmented Reality Advertising in 2025, which provides ROI frameworks for marketing executives.
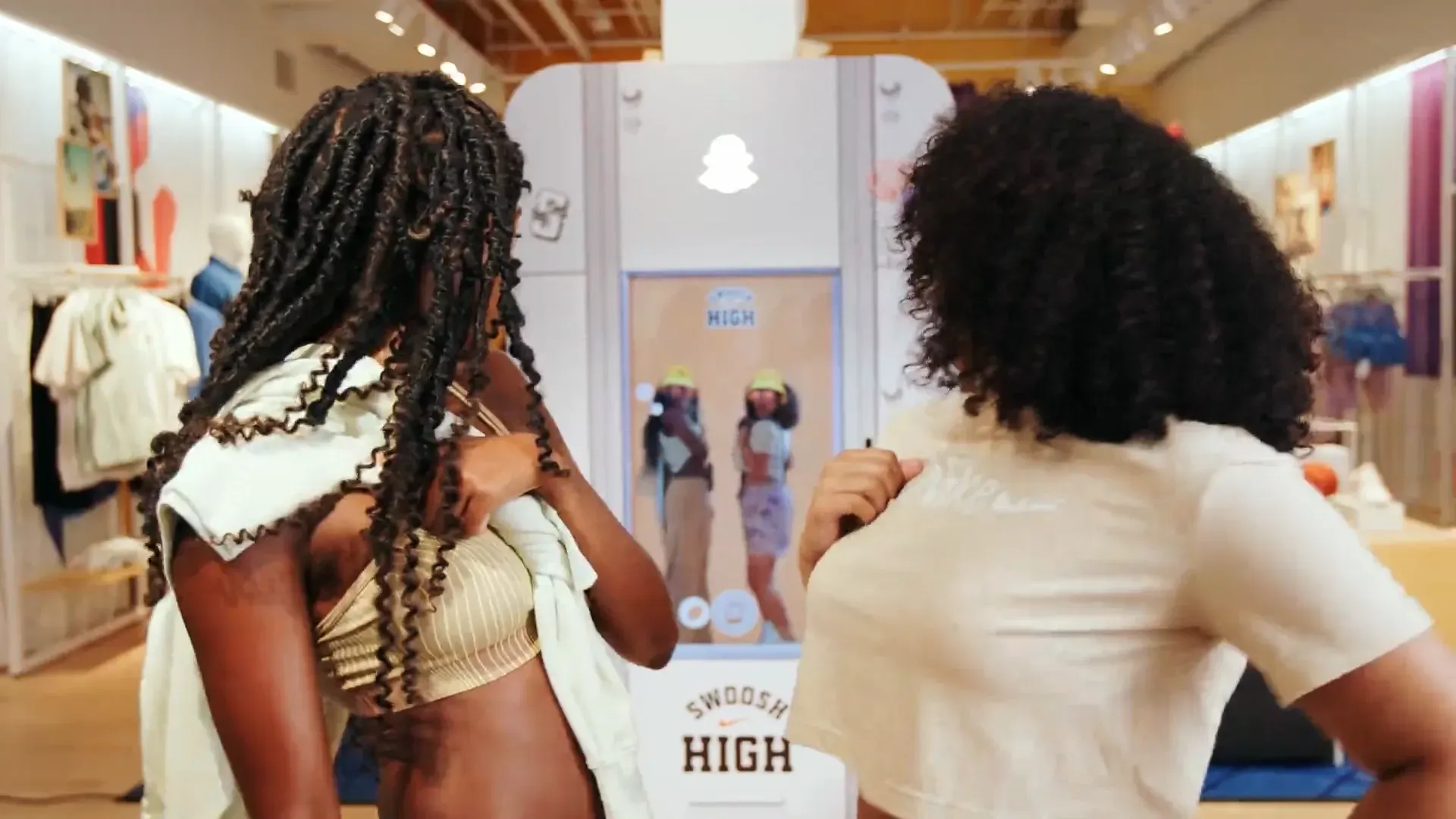
Augmented Reality (AR) “smart mirrors” are emerging as transformative tools in beauty retail, allowing customers to virtually try on makeup in-store with lifelike realism. Leading beauty retailers and brands—including Sephora, L’Oréal, and Estée Lauder—have launched and expanded AR mirrors to enhance the in-store experience, resulting in significant increases in sales conversion, basket size, and customer engagement. In-store AR mirrors address key issues, such as hygiene concerns, limited trial time, and choice overload, by enabling touchless, rapid try-ons of multiple products. The results are notable: Sephora’s AR mirror trials led to an estimated 31% increase in sales, and AR try-on users demonstrate conversion rates up to 90% higher than those who do not engage. Estée Lauder reports that AR experiences yield 2.5 times higher conversion for lipstick purchases, and Clinique’s AI-driven AR mirror increased basket size by 30% while extending dwell time five-fold. Major U.S. beauty chains are adopting AR mirrors as a strategic tool to drive in-store sales and customer loyalty, with international retailers (e.g., Watsons in Asia) experiencing double-digit sales growth after implementing AR mirror experiences. This executive case study examines the business case for in-store AR mirrors, the technology and ecosystem (key providers and partners), and detailed case studies of Sephora, L’Oréal, and Estée Lauder implementations. It also presents key ROI metrics and practical considerations for retail leaders looking to adopt AR mirrors. The evidence indicates AR mirrors are evolving from novelty to an essential part of an omnichannel beauty strategy, merging the convenience of digital try-ons with the tangible services of physical retail to enhance both customer satisfaction and profitability.
The Business Case for AR Mirrors
For beauty retailers, the in-store AR mirror offers an innovative solution to a longstanding challenge: how to enable customers to confidently try and buy cosmetics with minimal friction. Traditional in-store sampling has limitations — applying and removing multiple products is time-consuming and raises hygiene concerns. AR mirrors address this issue by allowing shoppers to “try on” numerous shades virtually in seconds, without ever touching their face. This establishes a safe and sanitary try-on process, a priority heightened by the pandemic. When testers were removed from many stores in 2020, AR mirrors and virtual try-on tools became essential alternatives, significantly accelerating the adoption of the technology.
From a business perspective, AR mirrors drive sales by enhancing customer confidence and encouraging exploration. By visibly “wearing” a new lip color or eyeshadow through AR, customers can discover products they might not have previously considered — effectively expanding their basket. Sephora found that AR experiences foster impulse purchases: its virtual mirror convinced shoppers to buy items they hadn’t initially planned on. The interactive and enjoyable nature of AR also keeps shoppers in the store longer, which generally correlates with higher spending. Industry reports indicate that immersive technology like AR can significantly increase dwell time in retail. In one instance, a beauty AR experience resulted in an average in-store dwell time of over 4 minutes, far exceeding typical engagements. Longer engagement provides more opportunities for associates to upsell and for customers to add items to their cart baskets.
Critically, AR mirrors address the “try-before-you-buy” expectation of modern consumers. Over 50% of consumers desire augmented shopping experiences to assist in product selection. By meeting this demand, retailers boost sales in the short term and cultivate brand loyalty. Shoppers view the brand as innovative and customer-centric. The novelty factor of AR mirrors — essentially a magic mirror that instantly showcases new looks — also creates buzz and foot traffic. Executives observe that these tech-driven experiences result in memorable store visits that attract shoppers, despite the convenience of online options.
From a financial ROI perspective, multiple data points highlight the business case. Marketing executives implementing AR strategies can quantify these benefits using our Augmented Reality OOH Advertising ROI Calculator, which helps model conversion improvements and revenue impact. The principles demonstrated in beauty retail apply broadly across AR advertising implementations, where similar conversion lifts and engagement metrics drive campaign success.Shopify reported that products featuring AR content experienced a 94% higher conversion rate than those without. Perfect Corp (a leading AR provider) commissioned a study revealing that AR try-on use made shoppers 1.6× more likely to purchase and to spend 2.7× more on cosmetics. In other words, AR-driven trials lead to higher conversion rates and increased average order values. These gains can directly enhance same-store sales. Beauty giant L’Oréal estimates that augmented reality and AI initiatives contributed to its e-commerce and in-store sales growth (52% e-commerce growth in 2019) by facilitating more personalized, confident purchases at scale. In summary, AR mirrors align with core retail KPIs: increasing conversion, basket size, dwell time, and customer satisfaction, all of which ultimately drive revenue and profitability.
Technology Overview
AR mirrors combine augmented reality software, cameras, and display screens in a fixture resembling a vanity mirror or digital kiosk. At the core is real-time facial tracking and rendering technology: a camera captures the customer’s face, and AR software overlays ultra-realistic 3D images of makeup (lipstick, eyeshadow, foundation, etc.) onto the live video feed. Unlike simple 2D photo filters, advanced AR mirrors utilize 3D facial geometry and AI to simulate how products appear from different angles and under various lighting. For example, ModiFace, a pioneer in beauty AR, calibrates its rendering by analyzing how makeup looks on models of different skin tones and lighting conditions, yielding a highly lifelike result. The goal is a virtual application that is nearly indistinguishable from real makeup application.
Early augmented reality (AR) mirrors were essentially large screens or tablets that ran AR try-on software. Sephora’s first installations between 2014 and 2016 featured 3D AR mirrors co-developed with ModiFace, which included a camera and screen housed in a vanity-like frame. Today’s implementations vary from full-length smart mirrors to iPad-based kiosks found at beauty counters. For example, the AR mirror launched by MAC Cosmetics in 2017 is a freestanding screen that maps the user’s face 30 times per second, realistically overlaying 30 different eye makeup looks. Other setups, such as Charlotte Tilbury’s “Magic Mirror,” utilize a mirror-shaped display with built-in lighting, evoking the ambiance of a glamorous vanity
Crucially, the tech has evolved to require no learning curve from shoppers: no app download or menu navigation is needed. Users simply stand in front of the mirror and see themselves with virtual makeup; the interface often lets them change shades with a simple gesture or tap, or even automatically recommends a look. Keeping the experience seamless is key to encouraging engagement, as noted by AR developers who avoid complex UIs to make mirrors universally inviting.
Behind the scenes, AR providers and tech partners create an ecosystem that enables these mirror experiences. In the beauty industry, several specialists stand out (see Table 1). ModiFace, acquired by L’Oréal in 2018, supplies AR and AI technology for makeup try-ons across many of L’Oréal’s 36 brands and has previously collaborated with Sephora and others. Perfect Corp., the maker of the YouCam Makeup app, offers a turnkey AR mirror solution used by retailers such as Ulta and Watsons; it features patented AgileFace® tracking for high accuracy. Agencies like Holition develop custom AR mirror experiences for luxury brands (e.g., Charlotte Tilbury) with tailored hardware and content. Newer startups (e.g., BrandXR) concentrate on pop-up AR installations for brands (as seen with Valentino Beauty and Makeup by Mario mirrors). These providers offer features ranging from virtual product try-ons to shade finders and integrated purchase functions (scanning a QR code from the mirror to add the product to the cart). Table 1 compares some leading AR mirror solutions and their notable brand deployments:
Table 1.
Leading In-Store AR Mirror Solution Providers and Deployments
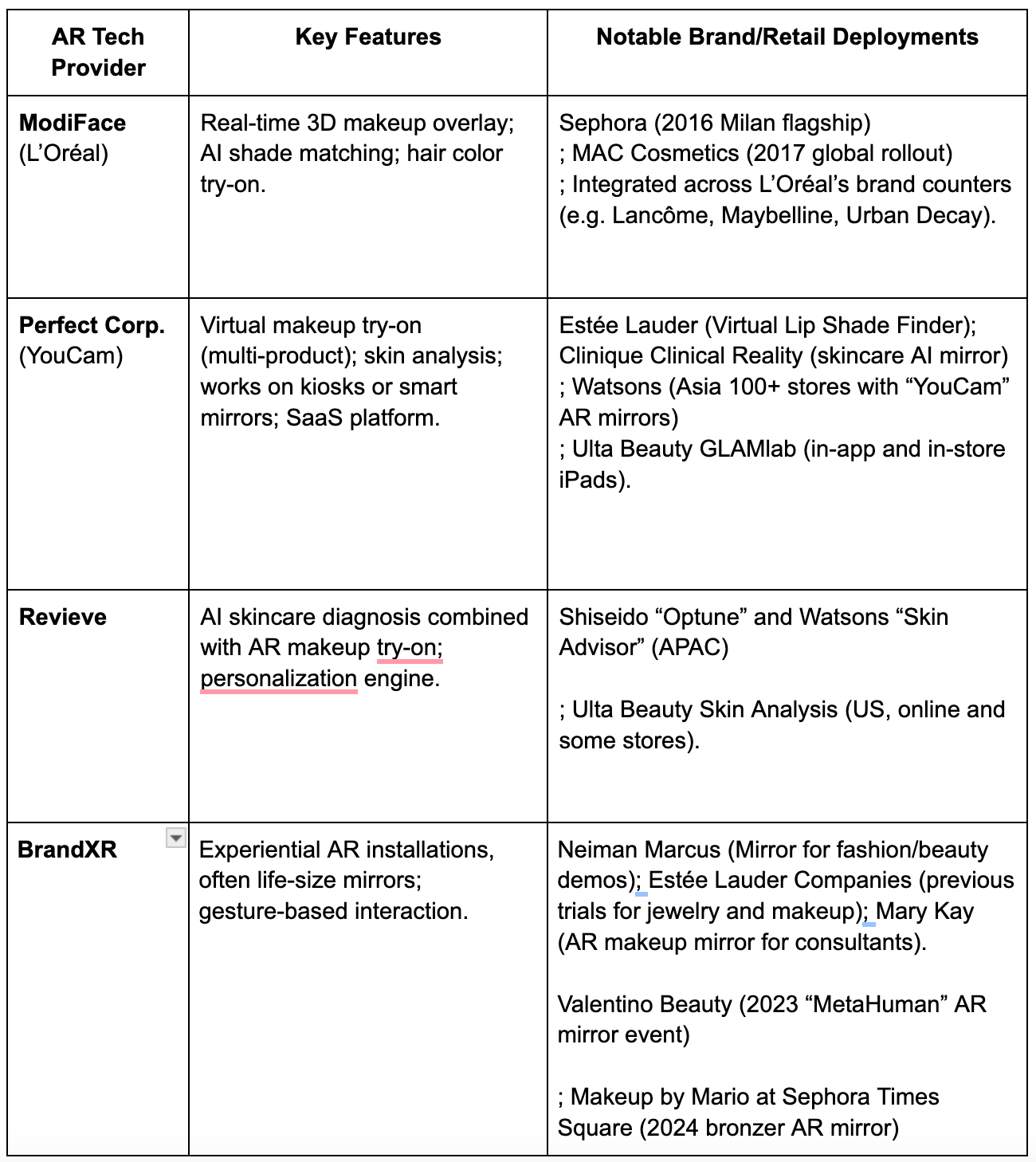
The integration of technology is typically collaborative: a brand or retailer partners with a tech provider to supply the software, while the hardware can consist of off-the-shelf touchscreens or custom builds.
Connectivity is also crucial — many AR mirrors are now linked to product databases so that when a customer finds a shade they like, the system can display availability or direct them to purchase (e.g., via QR code or by adding to a mobile app wishlist). Some even incorporate AI recommendations: Sephora’s Madrid flagship mirror uses AI to
detect a shopper’s attire and skin tone to suggest complementary products, merging AR with personalization. These innovations illustrate that AR mirrors are not just digital gimmicks but
fully
integrated retail tools that connect to inventory, CRM, and omnichannel shopping journeys.
Sephora: A First-Mover Advantage
Sephora is often credited as a trailblazer in beauty tech, and AR mirrors are no exception. As early as 2015, Sephora partnered with ModiFace to experiment with in-store AR, unveiling a 3D augmented reality mirror that could virtually apply makeup on customers’ faces in real time. This was first piloted in Sephora’s Milan store and at trade shows, generating buzz about the “future of cosmetics shopping.” The mirror tracked facial feature points and overlaid selected eyeshadow shades onto the live image. By tapping a shade on a screen, customers could see a photorealistic simulation on their own reflection instantly. For Sephora, known for its “try everything” ethos, this technology promised to enhance sampling without the mess or hygiene issues of physical trials.
Following the pilot, Sephora rolled out AR experiences more broadly via its Virtual Artist platform. In stores, this took the form of tablets and kiosks where customers or Beauty Advisors could use the AR try-on for lipstick and eyes products. By 2017, Sephora’s Virtual Artist (powered by ModiFace) was available on the Sephora mobile app and in select stores worldwide. This first-mover advantage allowed Sephora to gather early data on consumer engagement. The response was strong: globally, Sephora saw over 8.5 million visits to its AR experiences in the first 18 months. More importantly, those who tried on products virtually were substantially more likely to make a purchase. According to industry experts, Sephora’s virtual try-on users had 90% higher conversion rates compared to those who didn’t engage with the tool. As one report noted, immersive try-ons were “driving 90% higher conversion among users who engage” in Sephora’s case.
Sephora also leveraged AR mirrors for strategic marketing partnerships. In 2024, Sephora hosted a Makeup by Mario AR mirror at its flagship Times Square store as a limited-time activation. The 6-foot interactive mirror let shoppers virtually try the celebrity makeup artist’s new bronzer, guided by a video of Mario Dedivanovic “applying” the product on their reflection. This drew in crowds and media attention, underscoring Sephora’s image as an innovator. While short-term, the installation hinted at how AR mirrors can combine product education with trial: customers received a one-minute tutorial and shade match via the AR mirror, then could proceed to a physical station to test products or purchase. Foot traffic and engagement spiked during the activation, and though Sephora hasn’t publicly released sales figures, such experiential tech is known to lift sales for featured products. (For context, an AR campaign by Crocs in retail stores recently saw a 65%–122% sales lift for the promoted item, suggesting the power of AR to drive purchases when tied to a campaign.
Notably, Sephora’s AR mirror initiatives yielded insights beyond immediate sales. The company found that AR increased customer confidence and satisfaction. Consumers loved the ability to
quickly compare looks – trying a bold lipstick virtually gave them the courage to buy a shade they might not test otherwise. “It becomes a trigger for discovery and a catalyst for instilling purchase confidence,” one Sephora executive said about AR try-ons. Moreover, Sephora integrated the data from Virtual Artist into its marketing; popular shades tried in AR informed inventory and even influenced which products to run promotions on. By being first, Sephora also learned how to blend the AR mirror into the shopper journey seamlessly: for example, training beauty advisors to introduce the mirror as a fun service (rather than a replacement for personal assistance) was key to adoption. After using the mirror, customers could still consult an expert, combining high-tech and high-touch.
Financially, Sephora’s investment paid off. Sephora doesn’t break out exact numbers, but anecdotally the chain experienced
higher basket sizes when customers used digital tools in-store. One case study noted Sephora’s online orders saw a
35% increase in conversions when using virtual try-on; in-store, a similar impact was observed as mirror users often bought multiple shades. Parham Aarabi, CEO of ModiFace, noted, “interacting and virtually trying on makeup...lead to an increase in sales” and that in retail settings, a
mirror-like real-time 3D simulation is the ultimate marketing tool. His team reported that stores using the ModiFace AR mirror saw sales rise about
30% for the product categories featured. It’s telling that Sephora continued to expand AR features (Color iQ foundation matching, AI skincare diagnostics, etc.), which is a sign that the ROI was robust. By embracing AR mirrors early, Sephora solidified a high-tech reputation and
captured additional market share, especially among millennial and Gen-Z shoppers who flock to interactive, digital-native experiences. Sephora’s first-mover success paved the way for industry-wide adoption of AR mirrors.
L’Oréal: Scaling AR with In-Store Retailers
As the world’s largest cosmetics company, L’Oréal took a somewhat different approach – rather than using AR mirrors in its own stores (L’Oréal owns few standalone stores in the U.S.), it scaled AR through its portfolio of brands and retail partners. L’Oréal’s big move was the 2018 acquisition of ModiFace, making AR try-on a core internal capability. This allowed L’Oréal to roll out AR across dozens of brands and thousands of points of sale globally. For example, L’Oréal’s mass-market brands like Maybelline and L’Oréal Paris integrated virtual try-on screens in drugstores and big-box retailers. Upscale lines like Lancôme and Urban Decay (often sold at Ulta or Sephora) deployed tablets or kiosks running ModiFace’s software at their counters. By 2019, L’Oréal had equipped 20,000 stores with some form of AR cosmetics try-on, according to a company report (including mobile and in-store experiences).
One marquee example is NYX Professional Makeup (a L’Oréal brand), which opened tech-forward stores featuring AR makeup stations. NYX’s Color Factory stores let shoppers scan products and see them virtually on tablets/mirrors, blending the physical and digital shelf. L’Oréal also partnered with retailers on special AR experiences: in 2019 it teamed with Facebook and Amazon to bring ModiFace AR to retailer websites and pop-up displays. Through such partnerships, L’Oréal essentially embedded its AR mirror tech wherever its products were sold – both online and in brick-and-mortar.
The impact has been significant. Conversion rates rose sharply for L’Oréal products when AR try-on was used. L’Oréal’s chief digital officer noted that some AR makeup campaigns saw conversion lifts from 20% up to 80% above baseline. This means if normally 2 in 10 customers would buy after sampling, with AR it could jump to 3–4 in 10. Over millions of customers, that translates to substantial revenue. During 2020, when in-person trials were limited, L’Oréal’s virtual try-on usage skyrocketed – the company reported a 150% increase in virtual try-on sessions in 2020 vs 2019 as consumers embraced AR. And this trend continued: by 2023, L’Oréal saw over 100 million AR try-on sessions across its channels, up from 40 million the year before. This surge in usage contributed to e-commerce growth and also supported in-store sales as shoppers used “virtual try before physical buy” more routinely.
A concrete in-store example is L’Oréal’s collaboration with the Asian retail giant Watsons. Watsons installed Perfect Corp.'s AR makeup mirrors (featuring L’Oréal and other brands) in its Shanghai stores starting in 2017. By mid-2018, Watsons experienced double-digit sales growth (16–17% YoY) in China and credited innovations like the AR mirrors for attracting customers and enhancing conversion rates. Shoppers could virtually test L’Oréal lipsticks and eye palettes on the “Magic Mirror” and then pick them up directly in-store, bridging online convenience with offline immediacy. The AR mirrors became standard fixtures in Watsons’ new concept stores across Asia, often featuring L’Oréal’s product inventory.
For L’Oréal, owning ModiFace also meant being able to integrate AR in new ways. They developed an AI skin diagnostic (Vichy SkinConsult) and hair color try-on app (StyleMyHair), which are used at salons and beauty counters to complement the makeup AR mirrors. This broad approach ensures L’Oréal brands provide a high-tech consultation experience: a customer at a Lancôme counter can get a foundation shade match via AI, see it applied via AR mirror, and complete the purchase with confidence in the match. By 2021, L’Oréal stated that AR-driven services helped reduce product returns and improved customer satisfaction. They estimate deploying a centralized AR platform internally saved 50% of the cost compared to each brand doing separate solutions, highlighting an efficiency benefit.
From a sales perspective, L’Oréal’s embrace of AR mirrors is tied to an omnichannel strategy. The insights from AR usage are fed back into product development and marketing. For example, if virtual try-on data shows an unpopular shade, L’Oréal can adjust its lineup quickly. If certain colors trend in AR, they may increase production. L’Oréal’s CEO Nicolas Hieronimus noted AR is becoming “part of consumers’ habit” and an expectation. By meeting this expectation, L’Oréal’s brands stay competitive on retail shelves. They have even taken AR in-store beyond beauty: some L’Oréal-owned hair salons use AR mirrors for virtual hair coloring, and the company has experimented with AR fragrance discovery (where a smart mirror can suggest a perfume based on your outfit or mood). These initiatives further drive cross-selling and experiential shopping, encouraging customers to spend more time (and money) with the brand.
In summary, L’Oréal scaled AR mirrors not via its own stores but through a
network strategy – empowering its many brands and retail partners with leading AR technology. This has yielded measureable ROI: higher conversions (often double-digit percentage lifts), larger baskets, and valuable consumer data. It also fortified retailer relationships; L’Oréal became a partner that could bring cutting-edge tech to stores, thus securing better placement and promotions for its products. The AR mirror has become a standard part of L’Oréal’s sales toolkit, from the U.S. and Europe to China, giving the conglomerate a unified yet locally adaptable way to create
interactive in-store experiences at scale.

Estée Lauder: Premium Experience, Premium Results
The Estée Lauder Companies (ELC), which owns brands such as Estée Lauder, MAC, Clinique, Bobbi Brown, and La Mer, approached AR mirrors as a way to enhance the high-touch service model of prestige beauty. While L’Oréal emphasized scale, ELC focused on using AR to complement their consultants and luxury positioning. Early on, Estée Lauder partnered with various technology providers for different brands. MAC Cosmetics, renowned for its artistry, was among the first ELC brands to adopt AR mirrors in-store. In 2017, MAC introduced ModiFace-powered virtual try-on mirrors to all its U.S. stores, allowing shoppers to instantly preview over 20 makeup looks. MAC aimed to increase engagement and sales by making it easier for customers to experiment with bolder looks without hesitation. The global rollout in 2018 placed AR mirrors in hundreds of MAC locations, indicating strong initial results. MAC viewed this as a way to drive foot traffic from curious shoppers and provide its makeup artists with a new tool to engage customers. Even after virtually trying on looks, many customers would then have a MAC artist physically recreate the look, resulting in sales for each item used.
Meanwhile, the Estée Lauder brand, named after the company’s founder, took a slightly different approach to augmented reality (AR) by focusing on skincare and foundation. In 2018–2019, Estée Lauder launched the Virtual Shade Expert for its Double Wear foundation – an AR-driven tool on tablets designed to find your perfect foundation match and display it digitally on your face. Partnering with Perfect Corp., Estée Lauder reported that this innovation resulted in a 2.5× higher conversion rate for foundation purchases. Customers who utilized the virtual try-on feature to see their matched shade were significantly more likely to purchase than those who only conducted a manual swatch test. ELC noted enhanced customer loyalty from such AI/AR tools, as shoppers valued the accuracy and enjoyment of the experience.
Clinique, another ELC brand, launched an AR-based skin diagnostic called Clinical Reality that also functions as a smart mirror. This system scans the customer’s face- often at a department store counter or pop-up booth- and analyzes skin health, then virtually displays recommended skincare or concealer on the face. The outcomes from pilot deployments were impressive: Clinique saw a 150% increase in conversion (customers were 2.5 times more likely to purchase) among those who used the AR skin analysis mirror, a 30% higher average basket size, and 5× longer engagement time with the brand. These metrics underscore how a rich AR experience not only promotes a targeted product (like a serum) but also encourages customers to explore additional items (boosting basket size) and spend more time learning about their skin needs (increasing dwell time). For a premium brand like Clinique, this translates to a higher lifetime value per client.
Another standout is Bobbi Brown, which introduced “Artistry Like Never Before” AR mirrors in select stores. Bobbi Brown’s approach used AR for try-on and incorporated a tutorial element, where a virtual Bobbi Brown artist would appear on the mirror to give application tips. ELC found that this increased customer confidence in application techniques, leading to higher conversion, particularly for items like eye palettes that shoppers might feel unsure about. In fact, ELC’s CEO Fabrizio Freda mentioned that virtual consultations and try-ons carry up to 10× higher conversion than traditional in-store experiences for their brands. This was a broad statement during a 2020 earnings call, highlighting how powerful these digital try-on tools had become in driving sales conversion and even higher average order value.
For Estée Lauder Companies, AR mirrors are part of delivering a “premium experience. " They integrate these tools with consultant-led services: often, an AR mirror is used at the start to allow the customer to play and discover preferences, and then a beauty advisor steps in to fine-tune and provide samples or makeovers. This one-two punch has proven to yield premium results. For example, a customer might use the AR mirror to try five shades of Estée Lauder Pure Color lipstick, find a favorite, and then the advisor will apply it physically and recommend a matching lip liner and gloss — turning a single-item sale into a three-product sale. ELC has started quantifying such impacts, noting a higher units-per-transaction when AR is involved.
The ROI for ELC’s AR investments is also evident in clienteling and data. The company developed a central platform to implement AR across brands, similar to L’Oréal’s strategy. By 2021, ELC’s virtual try-on platform was supporting multiple brands rapidly and cost-effectively. Chris Aidan, VP of Digital Technology at ELC, noted that their in-house AR platform enabled them to launch new AR experiences in weeks, at half the cost of utilizing separate vendor solutions for each brand. This approach saved money and created a unified data stream. Data from MAC’s mirror and Clinique’s mirror flows into ELC’s CRM, informing personalized follow-ups, such as emailing a customer the selfie they took with a virtual look along with product links – a tactic employed by Sephora and MAC. These follow-ups further enhance online conversion after store visits, providing a genuine omnichannel benefit.
Finally, Estée Lauder Companies have utilized AR mirrors to reinforce a premium, technology-forward brand image. Luxury shoppers expect the best service; today, “best” includes high-tech features. AR mirrors in La Mer skincare suites or Tom Ford Beauty boutiques (Tom Ford is an ELC brand) provide an exclusive, cutting-edge experience. A study by a business school found that AI-powered makeup mirrors can actually enhance a sense of product value — customers linked the high-tech try-on with a higher-end experience, occasionally perceiving the products as more prestigious (though the same study warned that if executed poorly, AR can appear gimmicky). ELC has thus been diligent in ensuring their AR mirrors are hyper-realistic and on-brand (for example, the Charlotte Tilbury mirror – although ELC does not own Charlotte Tilbury, it’s a partner brand – was framed in rose gold and situated under chandeliers to match the luxury aesthetic aesthetic).
In summary, Estée Lauder’s deployment of AR mirrors has yielded impressive results aligned with its strategy: significantly higher conversions (often double or more), increased basket sizes for engaged customers, and longer engagement times. It enhances the premium service instead of replacing it, demonstrating that technology can amplify a human-centric sales approach. As a result, ELC entered the post-COVID retail era well-positioned, with AR mirrors and virtual try-on integrated into their retail model to provide contactless yet personalized service. The company’s digital leaders now view AR as a validated business tool, not merely an experiment, as it clearly drives both sales and customer satisfaction in their high-end retail environments.
Key Metrics and ROI
Across these case studies, several key performance indicators (KPIs) emerge as common measures of AR mirror success. Below, we summarize the before-and-after impact of in-store AR mirrors on sales and shopper behavior for leading brands:
Table 2.
KPIs Before vs. After Implementing In-Store AR Mirrors

As shown, improving conversion rates is the standout benefit of AR mirrors. Almost every brand reports increases in conversion of double digits or more. When shoppers try a product through AR, they gain confidence and are significantly more likely to make a purchase. For Clinique and Estée Lauder, conversion rates roughly doubled or more. Even where exact figures aren’t public (like Sephora and MAC), third-party analyses indicate substantial lifts (e.g., approximately 90% higher conversion for Sephora’s AR users). Sales lifts in the range of 20–30% for featured products are common, with some promotional cases seeing even higher spikes. Basket size can increase when AR encourages additional add-ons (Clinique saw a 30% increase). Extending dwell time is another positive: keeping customers engaged 3–5 times longer, as seen in Clinique’s case, not only makes the experience memorable but also provides more opportunities for recommendations products.
It’s also worth noting return on investment (ROI) in cost terms: while not shown in the table, brands have implied that AR mirrors pay for themselves through increased sales. For example, ModiFace’s AR integration cost brands $200k–$500k per year in licensing, but one successful implementation could easily generate far more in incremental annual sales across hundreds of stores. Moreover, the technology can reduce wasted samples and returns (if customers get the right shade the first time, they’re less likely to return it). ELC has pointed out that AR try-on lowers product return rates by boosting purchase accuracy, an often overlooked ROI factor.
Finally, adoption rates of AR mirrors are rising across the industry. Within the Fortune 1000 retail segment, a 2022 survey found that about 8% of specialty retailers had deployed AR mirrors in multiple stores, while over 25% were testing or planning to implement them in the next year (this number has likely grown post-pandemic). Regionally, adoption began in tech-forward markets (North America, Europe, East Asia) but is now expanding. Sephora and MAC’s global rollouts, along with Watsons in Asia and uptake by European chains like Douglas, indicate that AR mirrors are becoming mainstream in the beauty sector. The flagship store format is often where AR mirrors debut (to create a wow factor), after which they proliferate to top-tier stores and eventually to regular locations as hardware costs decrease. For example, Sephora’s smaller stores may not all have large AR screens, but they do provide beauty advisors with iPads running the same AR experience — effectively bringing the mirror to the customer hand.
Technology Partners and Ecosystem
Implementing AR mirrors requires navigating a tech ecosystem that spans hardware, software, and integration partners. Retail and marketing executives should understand the key players:
- Software Providers: As listed in Table 1, companies like ModiFace, Perfect Corp., and BrandXR lead the AR software space. These vendors offer SDKs or turnkey solutions that can be customized. Many beauty brands choose a provider based on realism of effects, breadth of features (e.g., can the same engine do makeup and skincare?), and analytics capabilities. It’s common for retailers to pilot with one vendor and later consider alternatives or even multiple providers for different needs.
- Hardware and Fixture Manufacturers: An AR mirror setup might involve custom enclosures, screens, and cameras. Some providers deliver an all-in-one unit (e.g., a “mirror” with built-in screen and lighting). Others rely on standard tablets or touchscreens that can be mounted in the store’s fixtures. Decisions here affect the aesthetic and maintenance. For a luxury brand, a bespoke mirror (as Charlotte Tilbury did, with antique-style mirrors housing screens) can reinforce branding. For a broad rollout, using durable tablets or kiosks might be more practical. Partnerships with fixture manufacturers or AV integrators can ensure the mirrors fit seamlessly into store design.
- Integration and IT: AR mirrors shouldn’t operate in isolation. Leading retailers integrate them with inventory systems (to reflect available shades), with e-commerce (so an in-store try can be saved to a customer’s online account or cart), and with analytics dashboards. This requires IT integration work.
APIs from AR vendors allow linking the try-on data to CRM systems. For example, if a loyalty member tries on products via the mirror and scans their membership, the retailer can record those preferences. Some companies partner with system integrators or digital agencies to connect these dots. Sephora SEA, for instance, worked with Braze to promote its AR feature and track user engagement across channels.
- Content and Product Data: To populate an AR mirror, a brand must have digital versions of each product (textures, colors, 3D models). This content creation can be done in-house or by the AR vendor. Companies like L’Oréal have dedicated teams to digitize each new product for ModiFace. Smaller brands might rely on the vendor’s scanning technology. Ensuring each product’s AR rendering is
true-to-life is crucial for trust — Makeup by Mario’s mirror succeeded by perfectly matching digital and physical bronzer shades. This often requires ongoing partnership; each season’s new products must be added promptly to the AR catalog.
- Ecosystem Partners: Beyond the mirror itself, AR in retail can involve partnerships with social media (Snapchat AR filters driving store traffic), with platforms like Google (which now features AR beauty try-on in search results), and with other brands. For example, a department store might implement one AR mirror that spans multiple beauty brands. This requires coordination on content and likely a neutral tech partner or a coalition approach (some retailers choose a single AR platform so all brands in-store adhere to it).
In this ecosystem, many Fortune 1000 retailers choose to pilot with a specialist partner. The partner can provide a full-stack solution for the trial, which the retailer tests in select stores while measuring results (conversion lift, usage rates, etc.). If KPIs are met, the rollout can expand, at which point integration into enterprise systems and possibly a more tailored solution might be pursued. It’s also important to ensure staff training and support from these partners. AR mirror providers often offer training modules for beauty advisors to become familiar with the technology and learn how to introduce it to customers naturally.
From a cost perspective, the ecosystem is evolving such that costs are decreasing. What used to require a multi-six-figure experimental budget can now be satisfied with a modest subscription or hardware lease. As one indicator, Holition advertises, “deploy to thousands of stores with no hidden costs,” suggesting scalable pricing models. Retailers can negotiate pilots that, if successful, transition into long-term contracts, possibly based on usage or the number of installations. Some beauty brands have even co-funded AR mirrors with retailers – for instance, a makeup brand might subsidize the mirror hardware on a department store's cosmetics floor in exchange for prominence. These creative partnerships make AR mirrors more accessible, even for retail chains concerned about upfront costs costs.
Implementation Considerations for Retail Leaders
For CEOs, CMOs, and marketing directors evaluating AR mirrors, several practical considerations should be top of mind:
- Define Objectives and KPIs: Identify what you want to achieve. Is the goal to lift sales of a particular category? Increase overall basket? Attract new customers or younger demographics? Clear goals will guide the choice of technology and content. For example, if the objective is
increasing lipstick sales by 15%, focus the AR mirror on lip try-on with as many shades as possible and measure conversion specifically for that category. As seen, Sephora focused on color cosmetics engagement, Clinique on skincare conversion – each tailored their AR content accordingly.
- Pilot and Measure in a Controlled Environment: Start with flagship or high-traffic stores to maximize data collection. Measure baseline metrics (sales, conversion, traffic, dwell time) and compare during the pilot. Ensure you have analytics from the AR software (e.g., number of try-ons per day, most tried products, session length). These can reveal insights – if dwell time is high but conversion isn’t, perhaps the content needs tweaking or staff need to better “close” the sale after a virtual try-on. One pro tip is to use A/B testing: have some stores with AR mirrors and similar control stores without, during the same period, to isolate the impact.
- Staff Training and Integration into Workflow: An AR mirror is most effective when store staff embrace it. Train beauty advisors to
invite customers to use it (“Would you like to see this new palette on you virtually?”) and to assist if needed. The mirror should augment, not replace, the salesperson’s role. Also plan the
operational flow: does the customer need to log in or can it be used anonymously? If they want to purchase, do staff use a connected tablet to add the item to the POS cart? Smooth integration here prevents any loss of momentum between virtual try-on and checkout.
- Content Management: Maintaining up-to-date and accurate virtual products is an ongoing effort. Ensure you have processes with the AR provider to add new product launches in a timely fashion (ideally before they hit stores). Outdated content can disappoint shoppers (“I want to try the new shade but it’s not on the mirror”). Additionally, consider seasonal or promotional content – e.g., special looks during holidays, or gamified AR experiences to collect a coupon – to keep the experience fresh. Makeup by Mario’s one-minute tutorial concept is a great example of enriching the content to boost engagement.
- Privacy and Data Handling: AR mirrors often involve cameras and possibly storing images (if users take selfies or share looks). Be transparent with customers about what data is collected. Many in-store AR experiences are designed to
not store personal images unless a user actively opts to save or share. Given rising concerns (e.g., Illinois’ Biometric Information Privacy Act has been cited in lawsuits regarding face-scanning tech in retail), legal teams should review the implementation. In Sephora’s case, their AR kiosk avoided retaining identifiable data to steer clear of privacy issues. If the implementation does collect data (like age or gender guesses for analytics), it should be anonymized. Clearly display a brief notice like “This smart mirror does not record or save your images. All processing is in real-time.”
- Physical Space and Infrastructure: Plan where and how the mirror will be installed. It needs proper lighting (many come with built-in lights) and a reliable power and internet connection (for cloud-based AR or analytics uploads). Allocate space such that it’s inviting but not obstructive. Some retailers put AR mirrors right at the entrance (to attract people in), others near the product displays (to encourage trial of specific items). The best location may depend on store layout and customer flow. Also, ensure durability – the unit will be touched and used frequently. Sturdy hardware and a maintenance plan (for cleaning the screen, etc.) are necessary.
- Promote and Incentivize Use: “If you build it, will they come?” Not always. Customers might be shy or unaware of the AR mirror at first. Use signage (“Discover your look here!”) and have staff actively mention it. Some stores run contests (e.g., “take a selfie with our virtual try-on and share on Instagram to win a gift card”) to spur initial use. As adoption builds, word of mouth will help. For Sephora SEA, a marketing push with in-app messages was needed to drive a
28% adoption increase of their AR feature. In-store, that might translate to in-person demos or integrating the AR mirror into beauty classes and events.
- Plan for the Future – Omnichannel Integration: Think long-term: AR mirrors can be a bridge between online and offline. Implementation should consider future integration such as linking with the retailer’s app (so a customer can continue trying products at home), or collecting email to send the customer the products they tried in a shoppable list. The
best ROI comes when the in-store experience doesn’t end at the store exit. For example, after using an AR mirror, a customer could get an email, “Here are the items you loved today, purchase anytime” with a special incentive. This leverages the in-store trial to capture online sales later, or vice versa. Estée Lauder’s strategy of building a unified platform allowed virtual try-on in video chats, on the web, and in-store to all share data — a model to aspire to.
By addressing these considerations, retail executives can greatly increase the likelihood of a successful AR mirror deployment. The technology is proven, but execution details make the difference between a gimmick that gathers dust and a powerhouse tool that consistently boosts sales and customer satisfaction.
What’s Next: The Future of AR in Beauty Retail
The rapid evolution of AR mirrors is poised to continue, bringing even more sophisticated capabilities to stores. Executives should keep an eye on emerging trends that could shape the next generation of beauty AR experiences:
- Full-Face and Multi-Product AR: Today’s mirrors typically apply one category at a time (e.g., lipstick or eyeshadow). Upcoming versions allow
full-face looks with multiple products layered simultaneously. This means a customer can virtually try an entire makeover (foundation, blush, eyes, lips all at once) – essentially a true virtual makeup artist. Sephora’s and Charlotte Tilbury’s systems are already moving this direction by offering curated looks (e.g., a “Smoky Eye Look” that includes various products applied together)
- Improved Realism and 3D Effects: As AR rendering improves, expect mirrors to handle things like glitter, shimmer, and textures with even more realism. For instance, simulating the reflective gloss of a lip gloss or the precise sparkle of an eyeshadow will get better with
physically-based rendering techniques (which Perfect Corp. and others are developing. Also, more accurate
color matching under different store lighting conditions will make the AR results virtually identical to real life. The aim is to eliminate any remaining gap between what the AR shows and what the product actually looks like on the customer.
- Personalized AI Recommendations: Future AR mirrors will likely double as AI beauty consultants. We’ll see deeper integration of
AI diagnostics (skin analysis suggesting a regimen, as Clinique does, or analyzing facial features to recommend contouring techniques, etc.). The mirror might say, “We suggest shade X for your skin tone and Y for your lip shape” – highly personalized advice generated instantly. In Madrid, Sephora’s AI mirror already reads aspects like the shopper’s outfit to tailor suggestions. Going forward, as AI models incorporate more data (personal preferences, past purchases), the recommendations will get smarter, potentially increasing conversion by focusing the customer on products they’re likely to love.
- Virtual Try-On + Physical Try-On Hybrid: A fascinating development is using AR to guide physical application. We might see AR mirrors that not only show a product virtually but then overlay instructions as you apply the real product (like an AR overlay showing where to tap the highlighter on your cheek). This hybrid approach merges the education aspect of AR with the tactile satisfaction of trying the product for real. It can also ensure customers use testers more hygienically or effectively (imagine a skin serum demo where the AR shows massage motions on your face). Brands like Lancôme have experimented with AR tutorials on mirrors for skincare application in Asia.
- Integration with the Metaverse and Social Shopping: The mirror in-store might transform into a portal for community and social features. Customers could view
peer reviews or photos of others with similar skin tones showcasing the product, displayed alongside their own AR reflection. Alternatively, they could scan a code to “take their AR avatar” into a metaverse app, allowing them to virtually try on looks from the comfort of home. With the growing excitement around the metaverse, stores could employ AR mirrors to enable customers to create content (e.g., a short video of themselves trying on a bold makeup look virtually) that can be shared — effectively converting the mirror into an in-store content creation booth. This could enhance word-of-mouth marketing.
- Cross-Category AR in a single mirror: We may also see beauty AR mirrors expanding to other retail categories in the same store. For example, a large department store could have a multipurpose AR screen – you try makeup, then maybe also see how a pair of sunglasses from accessories looks on your face, or how a hat from apparel fits. The technology fundamentals overlap, and it could maximize usage of expensive real estate. Already, some AR providers like BrandXR have mirrored that do both cosmetics and fashion try-on. Beauty could be the anchor that familiarizes customers with the interface, and then it extends to other uses (imagine “try the lipstick, then the necklace to go with it”).
The future will also bring cost reductions and smaller form factors. We might have AR mirrors the size of a compact or integrated into shelf edges. When AR can be delivered via standard tablets or even customers’ own phones with equal efficacy, retailers could opt for “bring your own device” AR experiences in-store (scanning a QR code on a regular mirror to activate AR on your phone). However, many executives believe having a dedicated in-store mirror provides a shared, branded experience that a phone alone cannot (and it avoids any app download barrier).
For beauty retailers aiming to stay ahead, it’s clear that AR is not a fad but a fundamental shift in how customers expect to experience products. Jeff Bezos often speaks about focusing on things that won’t change — in retail, one of those constants is that customers want to make sure a product is right for them. AR mirrors are simply a high-tech evolution of that truth, letting people virtually “try before buy” in an incredibly efficient way. The technology will keep improving, but the core benefit remains: more confidence, more convenience, more conversions.
In conclusion, AR mirrors have transformed from experimental pilots to
proven sales drivers in the beauty industry. U.S. brands like Sephora, L’Oréal’s collection, and Estée Lauder Companies have demonstrated real ROI, and some of the most impactful rollouts globally, such as Watsons and Charlotte Tilbury, indicate that this trend is worldwide. For Fortune 1000 retail and marketing leaders, the question is no longer “should we consider an AR mirror?” but rather “how soon and
how can we implement one effectively?” Those who thoughtfully embrace this technology are likely to see not only an uplift in sales metrics but also a strengthening of their brand’s innovative reputation — a crucial asset in a competitive retail landscape. The mirror on the wall may not literally declare who’s fairest of them all, but it will certainly help reveal which retailers are leading the future of beauty retail.
TALK TO A PRO
We're here to bring your brand to life!
Stay Connected with BrandXR
Create Augmented Reality for Free!
Create, Publish, and Measure 3D Augmented Reality Experiences Without Having to Code.














