Augmented Reality Solutions For Manufacturing
Augmented Reality for manufacturing no longer represents the future of the industry. Instead, this technology is being used today by businesses all over the world to improve operations. These use cases will show you how AR can be used to improve productivity, quality, and safety in manufacturing industries.
10 Augmented Reality Solutions for Manufacturing
1. Digital Twins
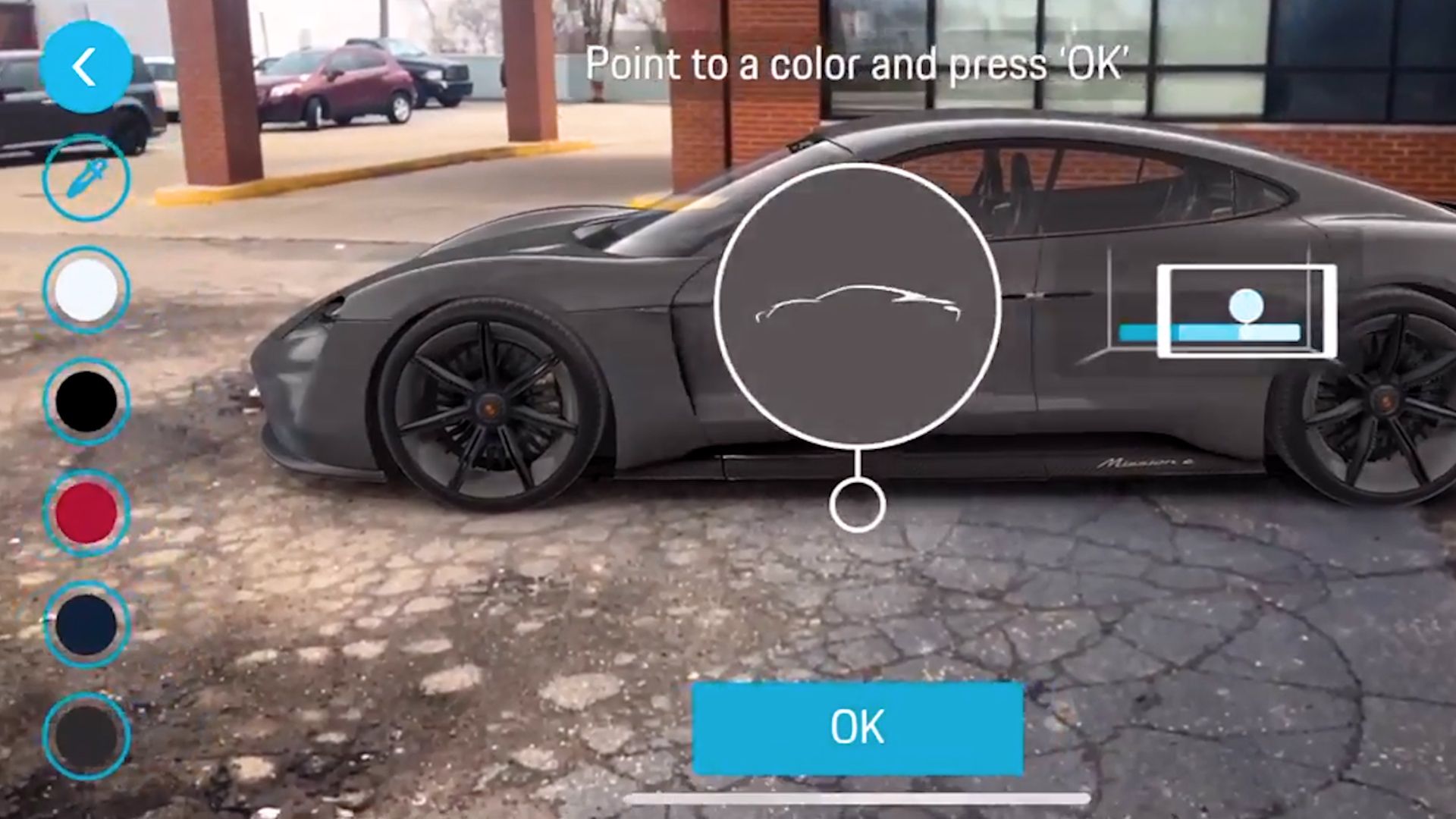
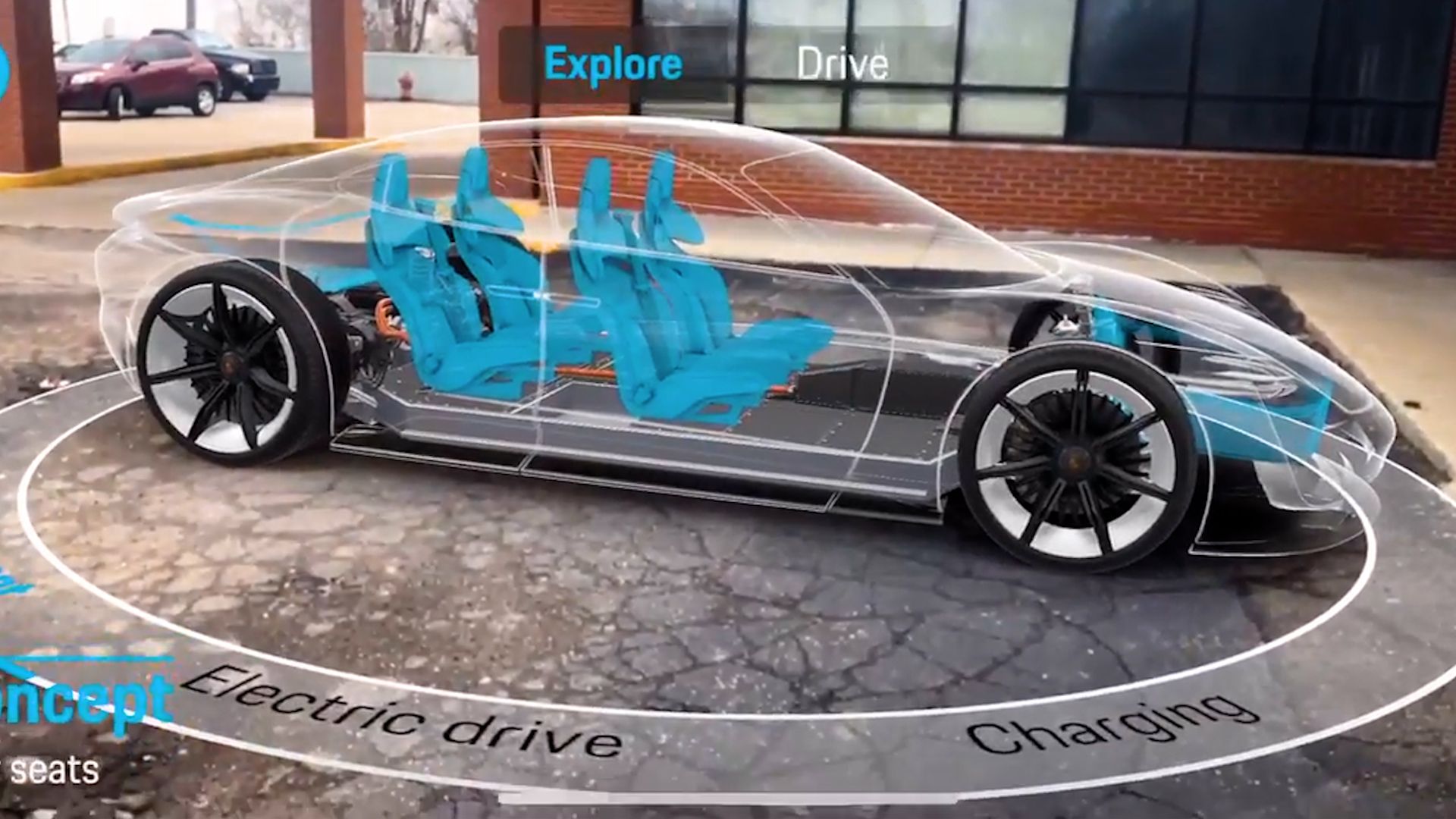
One of the fastest-emerging use cases for augmented reality for manufacturing is the creation of digital twins. AR allows those interested to design and build these true-to-life, digital representations of actual products. Digital twins, on their own, accelerate your time to market and improve training with your workforce. Augmented reality developers build these to allow anyone - from an engineer new to a project to the project’s creator - the ability to simulate any scenario they can think of. As a sales and marketing tool, it improves customer engagement and conversion with interactive and customizable 3D shopping experiences. The tech giant Siemens created a digital twin of its wind turbine system, allowing the company to test it out against hurricane-force winds without having to put its actual turbines at risk.

2. Product Design
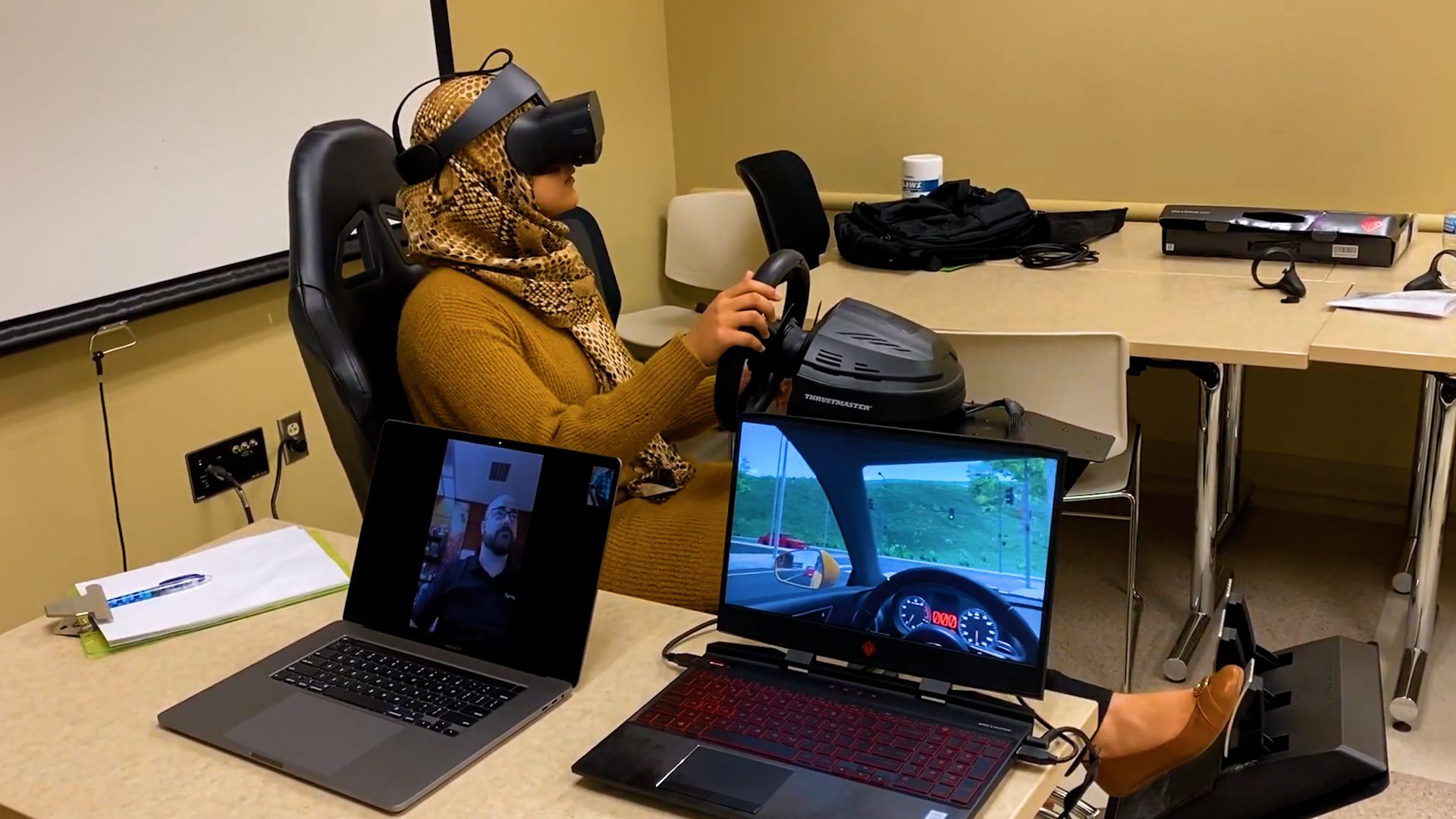
When it comes to product design, more businesses have turned to augmented reality in recent years. Augmented reality for manufacturing has proven to be a highly flexible technology. Ford uses Augmented Reality to help designers create new car models. With AR, designers can see a 3D model of the proposed car and make changes or adjustments as needed. This helps to improve the accuracy of designs and reduces the amount of time it takes to design a car.
3. Training and Instruction
Augmented reality for business can also enable increased productivity by using the technology to train employees and provide instruction on how to perform certain tasks. For example, Volkswagen uses AR devices to help employees learn how to assemble cars. Employees are given an AR headset that displays a 3D model of the car they will assemble. This allows them to see exactly where each part goes and how it should be assembled. These AR solutions help employees learn new tasks more quickly and reduces the chances of mistakes being made during complex assemblies like those in the automotive industry.
4. Inventory Management
How many items do you have on hand? Well, using augmented reality AR will help manufacturing plants and the workers there understand that in real time, no additional work instructions needed. Using augmented reality for manufacturing inventory management has become a newer, popular way to use the technology. That’s what Honeywell does. The company helps workers track inventory levels. Using an AR-enabled piece of equipment, workers can scan barcodes on products and see information about each product, including quantity on hand and location in the plant. This helps prevent shortages or overages of products.
5. Assembly Line Optimization
If you are looking to increase efficiency on assembly lines, AR is your technology. The luxury car manufacturer BMW uses Augmented Reality-enabled smart glasses that allow workers on the assembly line to see instructions and diagrams for each step of the assembly process. These AR glasses help workers understand what they are supposed to do and speeds up the assembly process overall, with comparatively little technical training needed.
6. Process Improvement
AR has also been used to improve processes in manufacturing. For example, Airbus uses AR to help engineers design aircrafts. With AR, engineers can see a 3D model of the proposed aircraft and make changes or adjustments as needed. This helps to improve the accuracy of designs and reduces the amount of time it takes through the product design stage an aircraft.
7. Quality Control
Using AR technology, business can enhance accuracy and speed in quality control. For example, Boeing uses an AR system to help inspectors verify that parts meet all requirements before they assemble their planes. With augmented reality for manufacturing, inspectors can view 3D models of parts and check for defects in real time, which means catching these defects before they become a problem in the real world. This helps speed up the inspection process and reduces the chances of defective parts being assembled into planes.
8. Process Troubleshooting
The German conglomerate ThyssenKrupp has been using augmented reality to help technicians troubleshoot problems with industrial equipment. Perhaps one of the more well-known applications of augmented reality for manufacturing, troubleshooting provides skilled technicians with a 3D model of the equipment to identify where a problem is happening. This helps speed up troubleshooting and reduces the amount of time it takes to fix the problem. This timeline will continue to shrink, too, as manufacturers and the tech industry address the skills gap in their workforce.
9. Maintenance Checks
AR can also be used for maintenance checks in manufacturing plants. GE uses augmented reality to help workers check for problems with gas turbines. With AR, workers can see a 3D model of the turbine and identify any problems that need to be fixed. This helps to speed up the maintenance process and reduces the amount of time it takes to fix a problem with a turbine.
10. Human-Machine Interface
Augmented Reality can also be used as a human-machine interface in manufacturing plants. McLaren uses Augmented Reality glasses and connected systems that allow workers on the assembly line to see instructions and diagrams for each step of the assembly process. This helps workers understand what they are supposed to do and speeds up the assembly process overall.
Drive Foot Traffic with Augmented Reality Murals
How It Works
Augmented Reality for manufacturing no longer represents the future of the industry. Instead, this technology is being used today by businesses all over the world to improve operations. These use cases will show you how AR can be used to improve productivity, quality, and safety in manufacturing industries.
01
Discover
A Creative Director will work with you on vision & visual targets, short-term and long-term goals.
02
Design/Develop
Working with our internal partners, we start to plan out how the experience will work with the technology and platforms’ requirements.
03
Test
This stage is all about making sure the experience meets the Goals & KPIs and is working as intended without any breaking issues. Internal testing is done during this phase.
04
Publish
This stage is all about getting the client’s final approval of the experience. Client provides confirmation they are happy with the final output and ready to proceed.